A number of receptors transmit signals from the extracellular space to the
intracellular compartment by means of a guanine nucleotide binding protein
(G-Protein) [20], e.g. adrenoceptors,
muscarinic cholinergic receptors ,
rhodopsin and the receptors for the antidiuretic hormone.
These receptors show certain similarities concerning their molecular
structure [21, 22] (see section genetics). They all
possess seven
membrane spanning domains, hence they are referred to as "seven membrane
spanning domain receptors".
These hydrophobic domains have a length of 20 to 24 amino acids. The
N-terminus of the
receptor and three loops are located extracellularly (EI - EIII),
the C-terminus and three loops extend intracellularly (CI - CIII).
The ![]() and
and ![]() adrenoceptors share 54% of their
sequence. The extracellular N-terminus contains several N-glycosylation
sites , the
inner loop CIII and the C-terminus carry phosphorylation sites
(see figure
figrecstruct). The membrane crossing sections are ligand binding
domains, the intracellular parts are bound to the G-protein.
The high variability of the C-III loop and the C-terminus seems to be the main
cause of the receptor specific aspects of binding the G-protein.
adrenoceptors share 54% of their
sequence. The extracellular N-terminus contains several N-glycosylation
sites , the
inner loop CIII and the C-terminus carry phosphorylation sites
(see figure
figrecstruct). The membrane crossing sections are ligand binding
domains, the intracellular parts are bound to the G-protein.
The high variability of the C-III loop and the C-terminus seems to be the main
cause of the receptor specific aspects of binding the G-protein.
Molecular biological studies revealed further subtypes of adrenergic
receptors [22], such as the
![]() ,
,
![]() [23, 24] types
of
[23, 24] types
of ![]() -receptors or the
-receptors or the ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() [25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32]
and
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32]
and ![]() types of the
types of the
![]() -receptor. Recently a
-receptor. Recently a ![]() -receptor of the fatty
tissue (termed
-receptor of the fatty
tissue (termed ![]() adrenoceptor) lacking phosphorylation sites was
discovered[33] .
All these subtypes can readily be divided into three groups by their molecular
biological characteristics.
adrenoceptor) lacking phosphorylation sites was
discovered[33] .
All these subtypes can readily be divided into three groups by their molecular
biological characteristics.
The human adrenoceptor subtypes are located on distinct
genloci ,
which happen to be rather close for ![]() and
and ![]() as well as
as well as ![]() and
and ![]() (see table 1.3).
(see table 1.3).
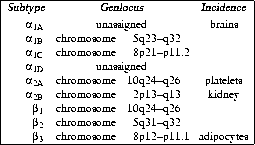
Table 1.3: Genloci of various adrenergic receptor subtypes